Additive Manufacturing
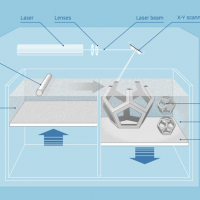
Additive Manufacturing by ferrous and non-ferrous metallic powders (from powder to solid) Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Printing machines for powder direct laser sintering work layer by layer as for all machines with additive logic. This is made possible by a suitable laser beam which is controlled through unattended and fully automated processes. With such systems the rapid manufacture of technical parts in defined materials is possible, both plastic and metal or sand. The laser used is high-power (typically 400 kW – 600 kW) and allows the sintering of polymer powders,...
Read MoreHot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
The hot isostatic pressing technique, often incorrectly called “hippatura”, is a production process developed since the ’70s and entered progressively in many industrial sectors, to reduce the porosity of metal aggregates and increase the density of many ceramic materials, with benefits in terms of increased resilience, fatigue behavior and workability. The main use of the HIP process is therefore to increase the density of the material (for the purposes and objectives for which this requirement is important) and the strength and structural reliability of the component. The...
Read MoreMetal Injection Moulding (MIM)
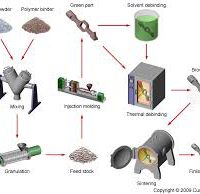
MIM process flow chart The production of “green” objects by injection molding of a metal powder in the polymer matrix has been developed in the 70s and initially used in the ceramics sector to be then adapted, ten years later, to the metal powders. In principle, the process is pretty simple (see figure). The metal powder is thoroughly mixed with a thermoplastic resin and processed with a kneading extruder or a roller to obtain the feed material plasticized, usually in granular form (feedstock). This material is injected into a heated mold in a similar way to what is done for the...
Read MoreCladding and Coatings
Laser cladding The laser deposition process (laser cladding) is an addition process of material on the surface of another in a controlled manner. A defined thermal power is furnished by means of a laser source, focused on the melting point and moved on the surface to be coated by automatic control, by depositing the coating material. The main advantages of this technique are: The possibility of depositing with extreme precision and localization new material with different features and characteristics with respect to the substrate; A wide range of couplings between different materials;...
Read More